Understanding Datadog logs preprocessing
If you are a user of Datadog’s log management product, you may already be familiar with logs pipelines and processors and how they can help extract your logs relevant data, enhancing search and allowing you to edit logs to enrich them with additional data.
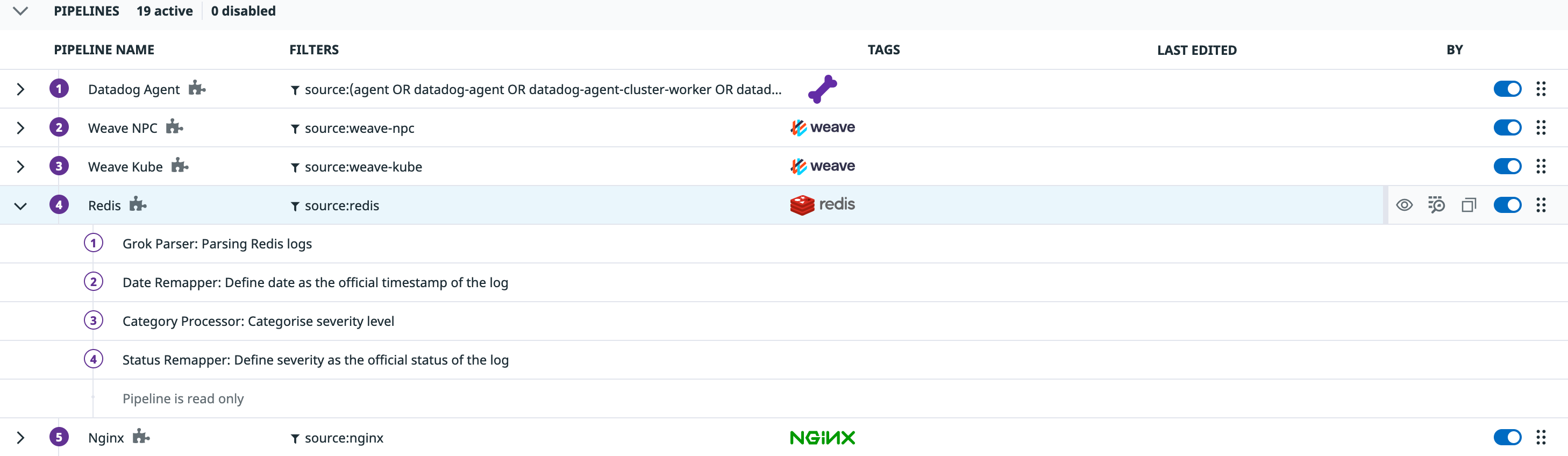
Pipelines are executed in order, meaning that the output log entry of a pipeline is the input of the next one, until there are no more enabled pipelines.
But what you may not know is that before a log entry goes through the different pipelines, there is an extra, special pipeline that processes the log entry if this comes in a JSON format, the JSON Preprocessing pipeline.
The JSON Preprocessing pipeline
There is a set of reserved attributes for logs at Datadog that are particularly important for log management and data correlation: date, host, service, status, traceid and message.
If the log entry is in JSON format, Datadog tries to parse those elements in the Preprocessing pipeline, before the rest of the pipelines parse the log entry. This pipeline cannot be disabled.
The attributes that will define those special parameters for your logs are predefined by Datadog. For example, if your JSON log has a host attribute, its value will be used as the host for this particular log entry.
If you are using the Datadog log agent or any of the default Datadog integrations, the log entries will come with the attributes that the Preprocessing pipeline accepts.
Changing the default attributes
If you are sending your logs from log shippers with different attributes or with custom attributes you can modify the Preprocessing pipeline to make sure that Datadog uses those custom attributes.
For example, if you have log entries with a server attribute and you want to use that attribute as the host in Datadog, you can modify the default attributes in the Preprocessing pipeline.
Navigate to Pipelines in the Datadog app and select Preprocessing for JSON logs:
You will get a modal window with the different attributes used for each of the parameters. They are ordered by precedence. For example, if your log entry has both a status and severity attributes, status will be used for “Status”, as it is the first one in that list.
You can add as many attributes as you need for each of the special parameters. In this example we are adding server to the host attributes:
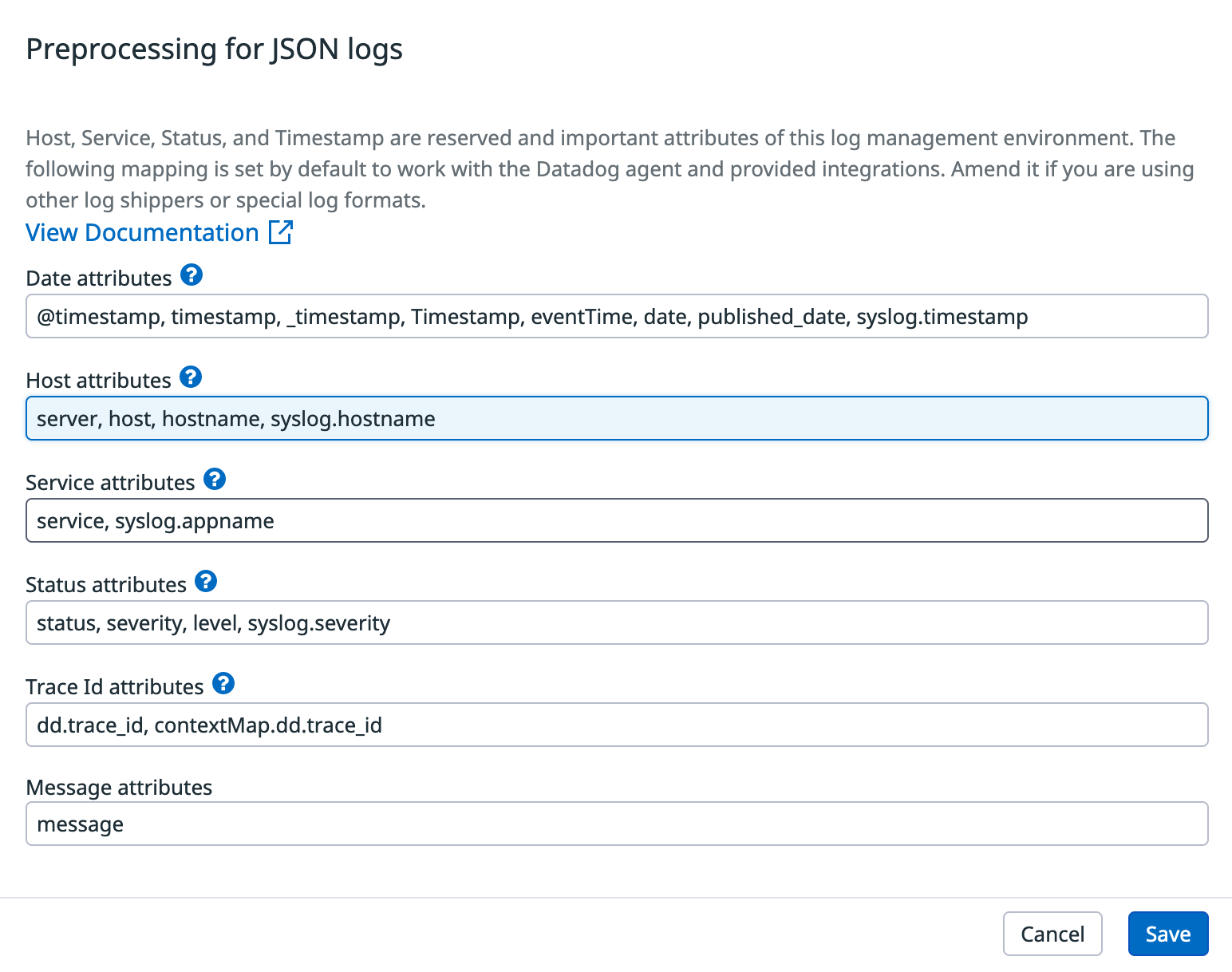
New processed logs with a server attribute will parse its content as host going forward.
The special host attribute
All reserved attributes are special, but host is even more special.
All other reserved attributes can be remap after the preprocessing pipeline, and that’s why we have a date remapper, status remapper, etc.
The host attribute is assigned during the preprocessing pipeline and cannot be modified later on. So, if you need to modify the attribute that assigns the host name, make sure to modify the preprocessing pipeline attributes.
Summary
When defining your log pipelines in Datadog it is always useful to know that there is a special pipeline that comes first, the Preprocessing JSON logs pipeline. Users can modify the attributes that are taken into account when parsing log entries with this pipeline.